
it is not necessarily a straight line from the starting position to the final location).
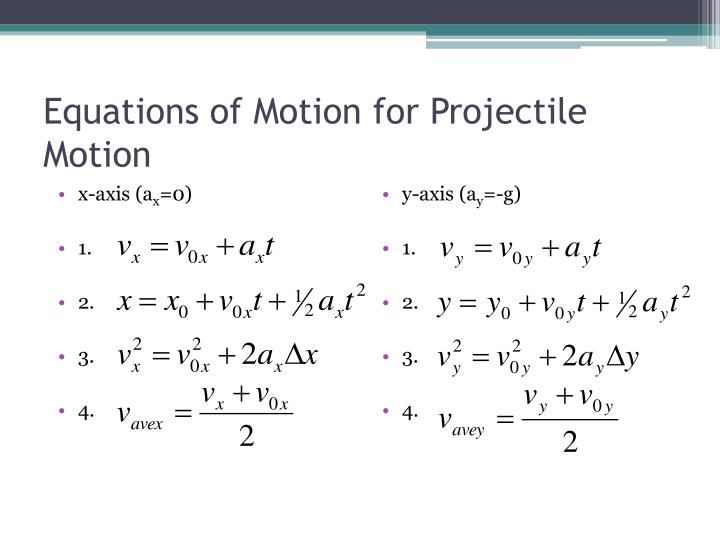
Here, we are assigning the upward y direction as positive, so a projectile experiencing the force of gravity, which pulls it in the downward y direction, will experience a negative velocity. The distance traveled is a a total distance traveled to the final position, not the displacement (i.e. For both x and y components, acceleration is constant, which allows us to use the kinematic equations.When writing out givens and determining what equation to use, this is key! KINEMATIC EQUATIONS: HORIZONTAL MOTION Since ax 0, the velocity in the horizontal direction remains constant (vx vox) and the position in the x direction can be determined by: xo+ (vox)(t) Why is a equal to zero (assuming movement through the air) KINEMATIC EQUATIONS: VERTICAL MOTION Since the positive y-axis is directed upward, ay -g. Only one of the equations does not include time.Projectile Motion Calculate Sound Pressure Level (SPL) at a distance R2 when the. kinematic equations for projectile motion Kinematics fundamentals : Sunil Kumar. This is used kinematics equation of uniformly acceleration motion. This "0" means "at t = 0," and x o and v o are typically pronounced "x-naught" and "v-naught." Equations of motion of a body moving with uniform acceleration along. Subscripts: "0" might be used for initial position and velocity instead of i.In one dimension, direction is typically indicated by signs – positive quantities are in the positive direction and negative quantities are in the negative direction. Position, velocity and acceleration are vector quantities, meaning they have direction associated with them.The angle between the velocity and acceleration in the case of. Sometimes the quantity x f - x i is written Δx, meaning “the change in x,” or even simply as d, meaning displacement. If the acceleration horizontally is zero, velocity must be constant, therefore v0 horizontally must equal v horizontally. The angular momentum of projectile mu cos × h where the value of h denotes the height.Note that x(t) does NOT mean x multiplied by t Depending upon which source you read, the final quantities may not have a subscript f, and/or might be represented in function notation as x(t) – read “ x as a function of time” or “ x at time t” – and v(t).

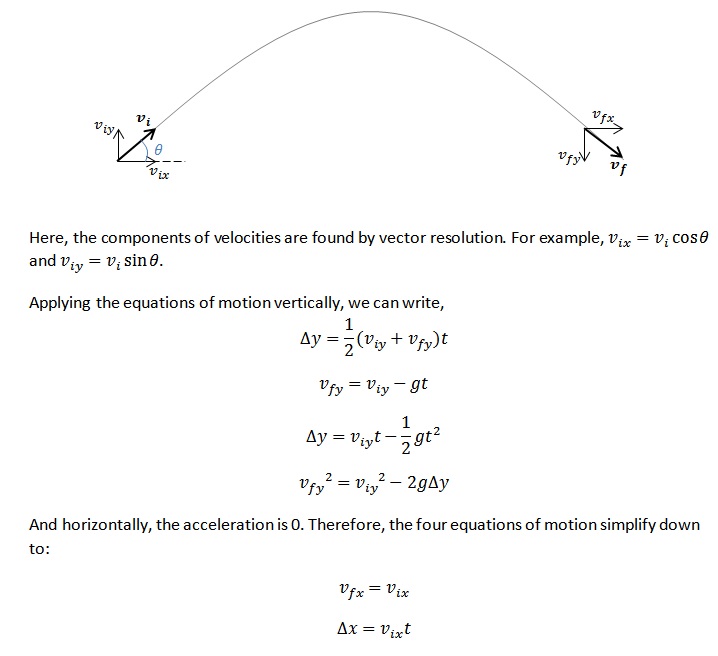
These kinematic formulas only work with a constant acceleration (which may be zero in the case of constant velocity).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
